
Selecting the correct fiber optic cable box depends on the conditions at the installation site. Outdoor Fiber Optic Boxes protect connections from rain, dust, or impact. A fiber optic box outdoor resists harsh weather, while a fiber optic box indoor suits clean, climate-controlled rooms.
Key Takeaways
- Choose fiber optic boxes based on the installation environment to protect cables from weather, dust, and damage or to ensure easy access and fire safety indoors.
- Check for durability, proper sealing, and compliance with safety standards to keep your network reliable and safe over time.
- Plan for capacity and future growth by selecting boxes that support easy expansion and good cable management to reduce downtime and maintenance costs.
Quick Comparison: Indoor vs. Outdoor Fiber Optic Boxes

Features Table: Indoor vs. Outdoor Fiber Optic Boxes
| Feature | Indoor Fiber Optic Boxes | Outdoor Fiber Optic Boxes |
|---|---|---|
| Environment | Climate-controlled, clean | Exposed to weather, dust, impact |
| Material | Lightweight plastic or metal | Heavy-duty, weatherproof materials |
| Protection Level | Basic dust and tamper resistance | High resistance to water, UV, and vandalism |
| Mounting Options | Wall, rack, or ceiling | Pole, wall, underground |
| Fire Rating | Often fire-rated | May include UV and corrosion resistance |
| Accessibility | Easy access for maintenance | Secured, sometimes lockable |
| Typical Applications | Offices, server rooms, data centers | Building exteriors, utility poles, outdoor enclosures |
Key Differences at a Glance
- Outdoor Fiber Optic Boxes withstand harsh environments. They use robust materials and seals to block water, dust, and UV rays.
- Indoor boxes focus on easy access and cable management. They suit spaces where temperature and humidity stay stable.
- Outdoor Fiber Optic Boxes often feature lockable covers and reinforced construction. These features deter tampering and protect sensitive connections.
- Indoor models prioritize compact design and fire safety. They integrate well with existing IT infrastructure.
Tip: Always match the box type to the installation site. Using the wrong type can lead to costly repairs or network downtime.
Key Factors When Choosing Outdoor Fiber Optic Boxes or Indoor Options
Installation Environment and Exposure
Selecting the right fiber optic box starts with a careful assessment of the installation environment. Outdoor Fiber Optic Boxes must withstand direct exposure to rain, dust, temperature swings, and even chemical contaminants. Manufacturers use weatherproof materials like UV-resistant plastics or aluminum to protect sensitive connections. Proper sealing with high-quality gaskets prevents moisture infiltration, which can degrade fiber optic performance. In contrast, indoor fiber optic boxes operate in climate-controlled spaces, so lighter and more cost-effective plastics are suitable. Site preparation also plays a role. Installers should avoid areas prone to moisture or extreme temperatures and ensure ventilation to prevent overheating. Regular maintenance, such as inspecting seals and cleaning fiber ends, helps maintain optimal performance.
Tip: Outdoor boxes should withstand thermal cycling and chemical exposure for long-term reliability.
- Outdoor boxes require high IP ratings and robust materials.
- Indoor boxes can use lighter materials due to reduced environmental risks.
- Proper sealing and site selection are critical for both types.
Protection, Durability, and Weather Resistance
Protection and durability define the difference between indoor and outdoor solutions. Outdoor Fiber Optic Boxes use heavy-duty materials and reinforced construction to resist physical impact and environmental hazards. For example, dual jacket cables provide an extra layer of defense against moisture, temperature changes, and mechanical stress. This enhanced protection reduces the risk of signal degradation and physical damage, ensuring reliable performance in harsh conditions. Indoor boxes, while less rugged, still offer basic dust and tamper resistance. The choice of material and construction should match the expected hazards at the installation site.
Location, Accessibility, and Ease of Installation
Location and accessibility influence both installation and ongoing maintenance. Installers often face challenges when placing fiber optic boxes in cluttered or hard-to-reach locations. Poor accessibility can complicate repairs and increase downtime. Best practices recommend selecting locations that avoid moisture and physical impact, ensuring secure connections, and labeling cables clearly for easier maintenance.
- Hard-to-reach or cluttered sites can cause future maintenance problems.
- Poor labeling complicates repairs, especially in complex environments.
- Different mounting options (wall, pole, rack) suit various environments and accessibility needs.
- Quality sealing and material selection remain critical for outdoor or harsh environments.
- Easy installation reduces errors and network downtime.
Capacity, Expandability, and Fiber Management
Capacity and expandability determine how well a fiber optic box supports current and future network needs. Effective fiber management practices, validated by industry standards like EIA/TIA 568 and ISO 11801, ensure reliable performance. Installers should use proper cable handling techniques, maintain appropriate pulling tension, and separate fiber from heavy copper cables. Support structures must comply with standards, and clear labeling helps with organization. Accessories such as hook and loop cable ties keep installations neat and reduce cable damage. These practices maintain cable performance and simplify future upgrades or repairs.
Note: Cable management tools and accessories help keep fiber optic installations organized, supporting long-term reliability.
Compliance, Fire Rating, and Safety Standards
Compliance with fire ratings and safety standards is essential, especially for indoor installations. Fiber optic cables must meet specific fire ratings such as OFNP, OFNR, and OFN, depending on their application area. These ratings exist to prevent fire propagation and reduce toxic smoke, which can pose serious risks in confined spaces. For example, Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH) jackets minimize hazardous emissions during a fire. The National Electrical Code (NEC) mandates different fire ratings for various building areas to protect occupants and property.
| NEC Fire Rating Code | Cable Type Description | Fire Resistance Level | Typical Application Areas |
|---|---|---|---|
| OFNP | Optic Fiber Non-conductive Plenum | Highest (1) | Ventilation ducts, plenum or return air pressurization systems (air circulation spaces) |
| OFCP | Optic Fiber Conductive Plenum | Highest (1) | Same as OFNP |
| OFNR | Optic Fiber Non-conductive Riser | Medium (2) | Vertical backbone cabling (risers, shafts between floors) |
| OFCR | Optic Fiber Conductive Riser | Medium (2) | Same as OFNR |
| OFNG | Optic Fiber Non-conductive General-Purpose | Lower (3) | General purpose, horizontal cabling areas |
| OFCG | Optic Fiber Conductive General-Purpose | Lower (3) | Same as OFNG |
| OFN | Optic Fiber Non-conductive | Lowest (4) | General purpose |
| OFC | Optic Fiber Conductive | Lowest (4) | General purpose |
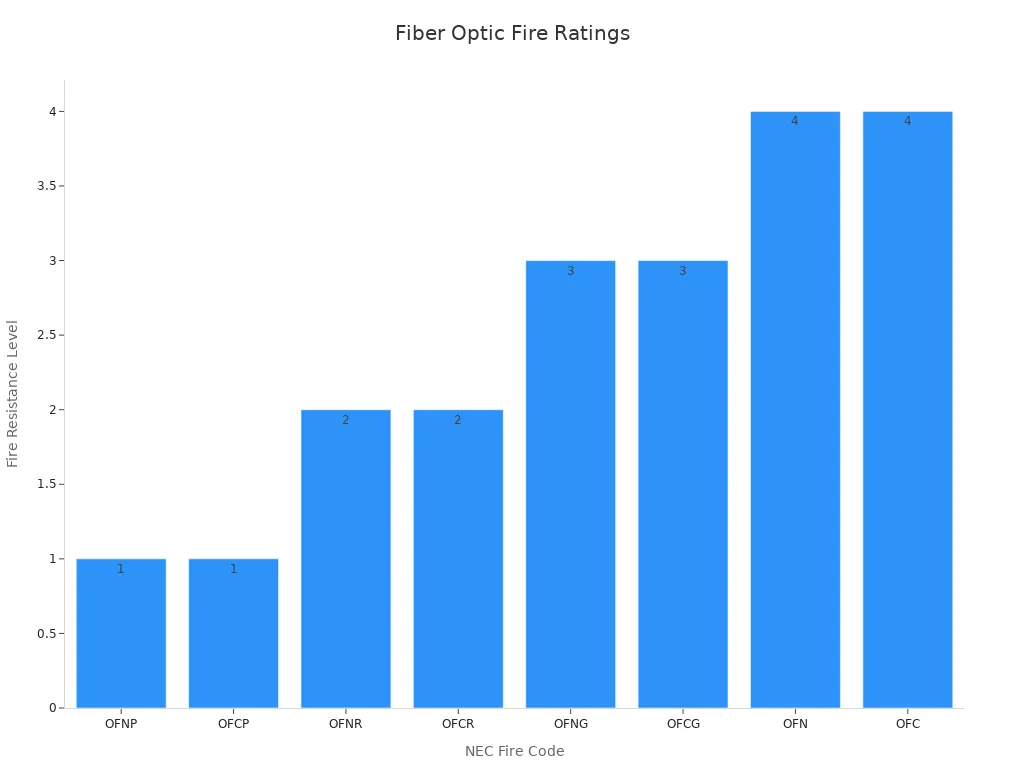
Plenum-rated cables (OFNP/OFCP) offer the highest fire resistance and are required in air circulation spaces to prevent fire hazards and toxic smoke spread.
Buyer’s Checklist for Indoor and Outdoor Fiber Optic Boxes
Assess Your Installation Site and Environmental Risks
A thorough assessment of the installation site forms the foundation of any fiber optic project. Environmental risks vary widely between indoor and outdoor locations. For example, a project in Yellowstone National Park required careful planning to avoid environmental impact, including burying fiber in conduit and relocating cell towers. Exposure to harsh weather, temperature swings, and moisture can degrade cables, leading to signal loss. Construction activities, wildlife interference, and corrosion in humid or salty environments also threaten cable integrity. Regular inspection and maintenance help detect vulnerabilities early, minimizing service disruptions.
Tip: Use protective enclosures and schedule routine checks to safeguard your network investment.
Determine Required Protection and Durability
Protection and durability requirements depend on the environment. Outdoor Fiber Optic Boxes must withstand rain, dust, and temperature fluctuations. Manufacturers use weatherproof materials like stainless steel or specialized plastics. Proper sealing prevents moisture ingress, which can damage cables. Products such as the FieldSmart® Fiber Delivery Point Wall Box meet NEMA 4 standards, demonstrating suitability for challenging conditions. Fiber optic boxes with enhanced weather resistance use waterproof enclosures, gel-filled tubes, and corrosion-resistant materials. These features ensure consistent high-speed connectivity and long-term reliability, even in high-risk areas.
Dowell offers a range of Outdoor Fiber Optic Boxes designed for maximum durability and protection, supporting network reliability in demanding environments.
Evaluate Capacity and Future Expansion Needs
Capacity planning ensures the fiber optic box supports both current and future network demands. Persistent coverage gaps, supply chain strains, and rapid growth in data centers highlight the importance of scalable solutions. Modular, pre-terminated assemblies and smaller form-factor connectors allow for higher fiber density without increasing space requirements. The global fiber management systems market is expanding rapidly, driven by rising bandwidth needs and the proliferation of IoT devices. Flexible, scalable systems help organizations adapt to future growth with minimal downtime.
Note: Choose fiber optic boxes that allow for easy expansion and support advanced management features.
Check Compatibility with Fiber Cables and Infrastructure
Compatibility with existing fiber cables and infrastructure is critical. Installation methods differ by environment. Outdoor cables may be direct buried, aerial, or installed in conduit, while indoor cables often use raceways or cable trays. Following manufacturer recommendations for pulling tension, bend radius, and handling prevents fiber damage. Hardware such as racks, cabinets, and splice panels should match the installation environment. Dowell provides comprehensive solutions that ensure seamless integration with both new and legacy infrastructure, reducing installation errors and supporting long-term performance.
Review Compliance and Building Code Requirements
Compliance with building codes and industry standards ensures safety and network integrity. Indoor fiber optic boxes must meet standards such as TIA-568 and ISO/IEC 11801, which govern design, installation, and maintenance. Proper cable management and high-quality materials are essential for reliable indoor networks. Outdoor installations require adherence to local codes and environmental regulations, including weatherproofing, burial depth, and protection against UV exposure and physical damage. Institutions like UA Little Rock enforce strict compliance, requiring detailed documentation and testing to guarantee infrastructure reliability.
Always verify that your chosen fiber optic box meets all relevant codes and standards for your region.
Match Features to Indoor or Outdoor Fiber Optic Boxes
Selecting the right features depends on the installation environment. Outdoor Fiber Optic Boxes need robust construction, weatherproof seals, and enhanced security features such as lockable covers. Indoor boxes should prioritize compact design, fire safety, and easy access for maintenance. Use sealed splice closures outdoors and patch panels or wall-mounted boxes indoors. Dowell’s product line includes both indoor and outdoor options, allowing buyers to match features precisely to their site requirements.
Balance Budget with Required Features
Budget considerations play a significant role in the selection process. High deployment costs, regulatory hurdles, and skilled labor shortages can impact project timelines and expenses. Innovations such as microtrenching and modular assemblies help reduce costs and speed up installation. Federal and state funding programs may support fiber expansion in underserved areas. Buyers should balance initial investment with long-term reliability, protection, and scalability.
Investing in quality fiber optic boxes from trusted suppliers like Dowell ensures value and performance over the life of your network.
Common Scenarios for Indoor and Outdoor Fiber Optic Boxes

Typical Indoor Applications
Fiber optic boxes serve a wide range of indoor environments. Offices, data centers, and server rooms often require secure and organized cable management. These locations benefit from wall-mounted or rack-mounted boxes that keep fiber connections safe from accidental damage and unauthorized access. Educational institutions and hospitals use indoor fiber optic boxes to support reliable internet and communication networks. In these settings, technicians can easily access and maintain connections due to the controlled environment. Compact designs and fire-rated materials help these boxes blend into existing infrastructure while meeting safety standards.
Note: Indoor fiber optic boxes simplify network upgrades and routine maintenance, reducing downtime in mission-critical facilities.
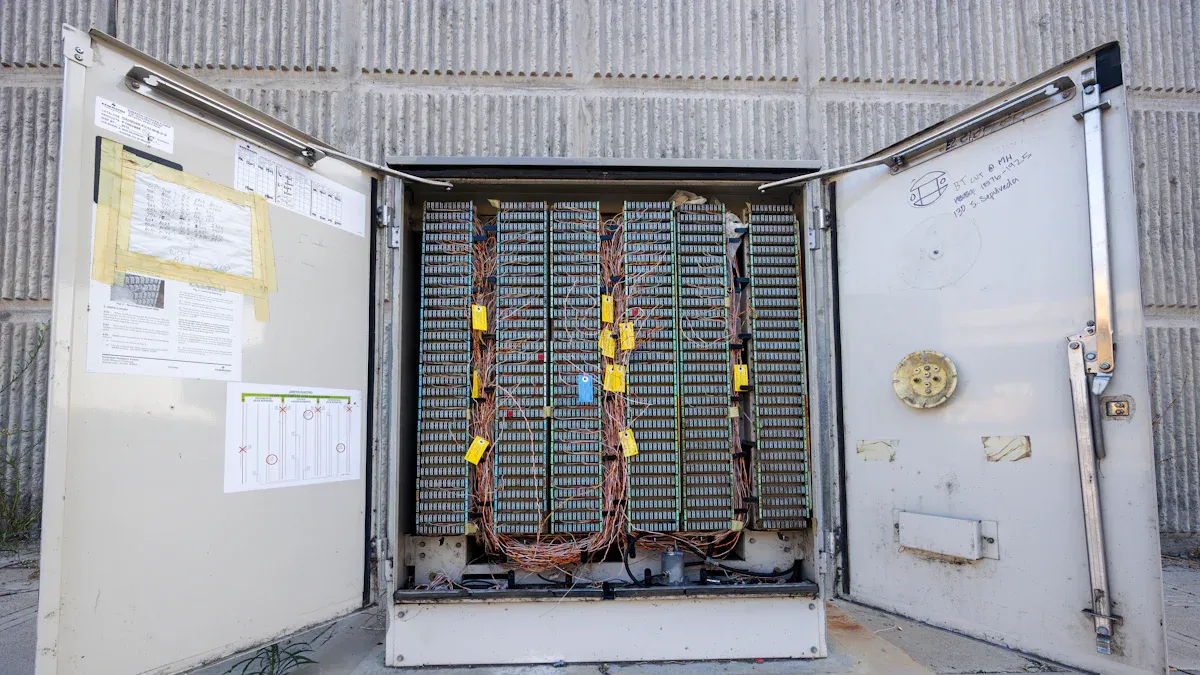
Typical Outdoor Fiber Optic Boxes Use Cases
Outdoor Fiber Optic Boxes play a crucial role in environments exposed to weather, physical impact, and temperature extremes. Utility poles, building exteriors, and underground installations all require robust protection for fiber connections. Field experiments have shown that optical fiber sensors, when placed in watertight boxes and reinforced soil, can withstand dynamic and seismic loads. These sensors maintained accuracy even under accelerations up to 100 g, proving the reliability of outdoor installations in harsh geotechnical conditions.
In ecological monitoring, fiber-optic distributed temperature sensing systems have delivered precise temperature data across multiple stream sites. These systems provided superior coverage and accuracy, supporting sensitive applications like fisheries habitat selection. Outdoor Fiber Optic Boxes enabled these advanced technologies to function reliably, even in challenging environments with fluctuating temperatures and moisture.
- Utility companies use outdoor boxes for network distribution in rural and urban areas.
- Environmental agencies deploy fiber optic systems for real-time monitoring in remote locations.
- Construction projects rely on outdoor boxes to protect connections during site development.
The installation environment determines the best fiber optic box for any project. Selecting boxes with high reliability metrics, such as strong weather resistance and low insertion loss, reduces downtime and maintenance costs. Using the buyer’s checklist helps organizations achieve long-term network performance, safety, and value.
By: Lynn
Tel: +86 574 86100572#8816
Whatsapp: +86 15168592711
E-mail: sales@jingyiaudio.com
Youtube: JINGYI
Facebook: JINGYI
Post time: Jul-07-2025
