Importing Fiber Optic Cables from China with assured quality is entirely feasible. Diligent supplier vetting and strict adherence to industry standards are crucial for securing high-quality products. The global fiber optic cable market, valued at approximately USD 13.46 billion in 2024, underscores the importance of reliable sourcing. A strategic approach makes high-quality imports possible.
Key Takeaways
- Choose a good manufacturer. Make sure they have proper certifications and clear communication.
- Know what you need. Specify the cable type, materials, and how much signal loss is okay.
- Check the cables before they ship. This helps find any damage early and saves money.
Selecting a Reputable Manufacturer for Quality Fiber Optic Cable
Securing high-quality Fiber Optic Cable begins with selecting the right manufacturing partner. This crucial step involves careful vetting to ensure reliability and product integrity. Buyers must distinguish between genuine manufacturers and mere traders.
Verifying Manufacturer Credentials and Avoiding Traders
A direct manufacturer offers significant advantages over a trading company. Manufacturers possess direct control over their production processes, quality assurance, and technical specifications. Traders, conversely, act as intermediaries, often adding markups and lacking direct oversight. Understanding these differences helps buyers make informed decisions.
| Feature | Fiber Optic Cable Manufacturer | Trader |
|---|---|---|
| Production Control | Direct control over production schedules and quality control | Lacks direct control over production schedules and quality control |
| Pricing | Direct factory-gate price, no middleman markup | Adds a markup (typically 10-15%) |
| Customization | Offers customization (e.g., printing brand logo, specific fiber counts) | May not offer direct customization or has limited options |
| Technical Knowledge | Possesses engineering teams, can provide detailed technical data (e.g., attenuation loss reports) | Often lacks in-depth technical knowledge, may need to consult others |
| Transparency | Can provide live video tours of production floor | May make excuses for video calls, generic office appearance |
| Certifications | Can provide and verify ISO 9001 certificates matching bank account | May have difficulty verifying certifications or matching names |
Reputable manufacturers, like Dowell, demonstrate their legitimacy through comprehensive certifications and transparent operations. Buyers should request specific documentation to verify a manufacturer’s adherence to industry standards. Key certifications include:
- IEC 60794: Requirements for optical fiber and cable elements.
- Telcordia GR-20: Generic requirements for Outside Plant (OSP) optical fibers and cables.
- ISO 9001:2015: A quality management system indicating commitment to high standards and inspection criteria.
- RoHS: Compliance with the Restriction of Hazardous Substances.
- UL 94 Certification: For flammability of plastic materials in components.
- CE, UL, and ETL: Various product safety and performance certifications.
Verifying these certifications often involves checking the certificate number against the issuing body’s online portal. For ISO 9001, buyers can verify through members of the International Accreditation Forum (IAF). This diligence ensures the manufacturer meets recognized quality and safety benchmarks.
Conducting Thorough Factory Audits for Fiber Optic Cable Production
A factory audit provides direct insight into a manufacturer’s capabilities and quality control processes. This on-site inspection is essential for assessing production facilities and operational standards. A comprehensive audit checklist covers numerous aspects of fiber optic cable production. Key areas include:
- Raw Material Inspection: Verifying the quality of incoming components.
- Manufacturing Process Checklist: Reviewing fiber drawing, coating, coloring, buffering, and jacketing procedures.
- Quality Control Documentation Review: Examining test reports for tensile strength, diameter, attenuation, and end-face quality.
- Equipment Calibration Log: Ensuring all testing and production equipment receives regular calibration.
- Packaging and Storage Guidelines: Assessing how finished products are handled and stored.
- Environmental Testing Protocol: Checking for compliance with environmental standards.
During an audit, buyers should watch for several red flags. Manufacturers providing vague equipment descriptions, such as “modern, advanced equipment,” without specific details (e.g., “12 coloring lines with speeds up to 600 meters/minute”) raise concerns. Pricing significantly below market rates, sometimes 40% or more, often indicates substandard materials or misrepresented specifications. Furthermore, a lack of standardized test report templates for attenuation, return loss, and length verification suggests inconsistent testing practices. Buyers should also inquire about market constraints, such as helium shortages affecting fiber production or tariff reshuffles impacting component sourcing, as these can influence pricing and lead times.
Assessing Communication and Support for Fiber Optic Cable Orders
Effective communication and robust support are vital throughout the procurement process. A reputable manufacturer provides clear, timely, and accurate information regarding orders, technical specifications, and potential issues. They offer dedicated technical teams capable of answering detailed questions about product performance, installation, and compliance.
Manufacturers should provide responsive customer service, addressing inquiries promptly and offering solutions to any challenges that arise. This includes transparent updates on production schedules, shipping logistics, and post-sales support. Strong communication fosters trust and ensures that the final product meets all specified requirements and expectations.
Defining Critical Specifications for Your Fiber Optic Cable

Defining precise technical specifications is paramount for successful Fiber Optic Cable imports. Clear specifications ensure the manufacturer produces a product meeting exact performance requirements. This proactive approach prevents misunderstandings and guarantees quality.
Specifying Fiber Optic Cable Type and Core Brand
Buyers must clearly specify the Fiber Optic Cable type. Different applications require distinct cable characteristics. For instance, single-mode fiber (SMF) supports long-distance, high-bandwidth transmission, suitable for metro networks and backbone infrastructure. Multimode fiber (MMF) serves short-distance applications like LANs and data centers.
| Feature | Single-mode fiber (SMF) | Multimode fiber (MMF) |
|---|---|---|
| Core Size | Small (around 8–10μm) | Larger (50μm or 62.5μm) |
| Light Paths | Supports one light mode | Supports multiple light paths |
| Transmission | Long-distance, high-bandwidth | Short-distance |
| Common Usage | Metro networks, long-haul communications, backbone | LANs, campus networks, inside data centers |
| Types | OS1, OS2 (OS2 optimized for outdoor long-distance) | OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4, OM5 (OM1/OM2 rarely used, OM4 prevalent) |
Other classifications include simplex or duplex by fiber count, OFNR or LSZH by cable jacket, and various connector types like LC, SC, or APC polishing. Specifying the fiber core brand is also critical. Leading global brands include Sumitomo Electric Industries, Fujikura Ltd., Furukawa Electric Co., Ltd. (OFS), YOFC, Prysmian Group, and Corning Incorporated. These brands offer superior performance and reliability.
Insisting on Virgin Jacket Materials for Fiber Optic Cable Durability
The cable jacket protects the delicate optical fibers within. Insisting on virgin jacket materials, rather than recycled ones, ensures maximum durability and longevity. Virgin materials provide consistent physical properties, including tensile strength, flexibility, and resistance to environmental factors like UV radiation, moisture, and extreme temperatures. Recycled materials often have inconsistent properties, which can lead to premature degradation and failure, compromising the cable’s performance and lifespan.
Checking Fiber Optic Cable Attenuation and Loss Specifications
Attenuation and loss are critical performance indicators for Fiber Optic Cable. The Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) and Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) standards define these requirements. Maximum attenuation, measured in dB/km, represents the signal loss over distance.
| Fiber Type | Wavelength (nm) | Max Cable Attenuation (dB/km) |
|---|---|---|
| OM3 Multimode | 850 | 3.0 |
| OM3 Multimode | 1300 | 1.5 |
| OM4 Multimode | 850 | 3.0 |
| OM4 Multimode | 1300 | 1.5 |
| OM5 Multimode | 850 | 3.0 |
| OM5 Multimode | 953 | 2.3 |
| OM5 Multimode | 1300 | 1.5 |
| Indoor/Outdoor Single-mode | 1310 | 0.5 |
| Indoor/Outdoor Single-mode | 1383 | 0.5 |
| Indoor/Outdoor Single-mode | 1550 | 0.5 |
| OS1a Inside Plant Single-mode | 1310 | 1.0 |
| OS1a Inside Plant Single-mode | 1383 | 1.0 |
| OS1a Inside Plant Single-mode | 1550 | 1.0 |
| OS2 Outside Plant Single-mode | 1310 | 0.4 |
| OS2 Outside Plant Single-mode | 1383 | 0.4 |
| OS2 Outside Plant Single-mode | 1550 | 0.4 |
Additionally, buyers must consider insertion loss for connectors and splices.
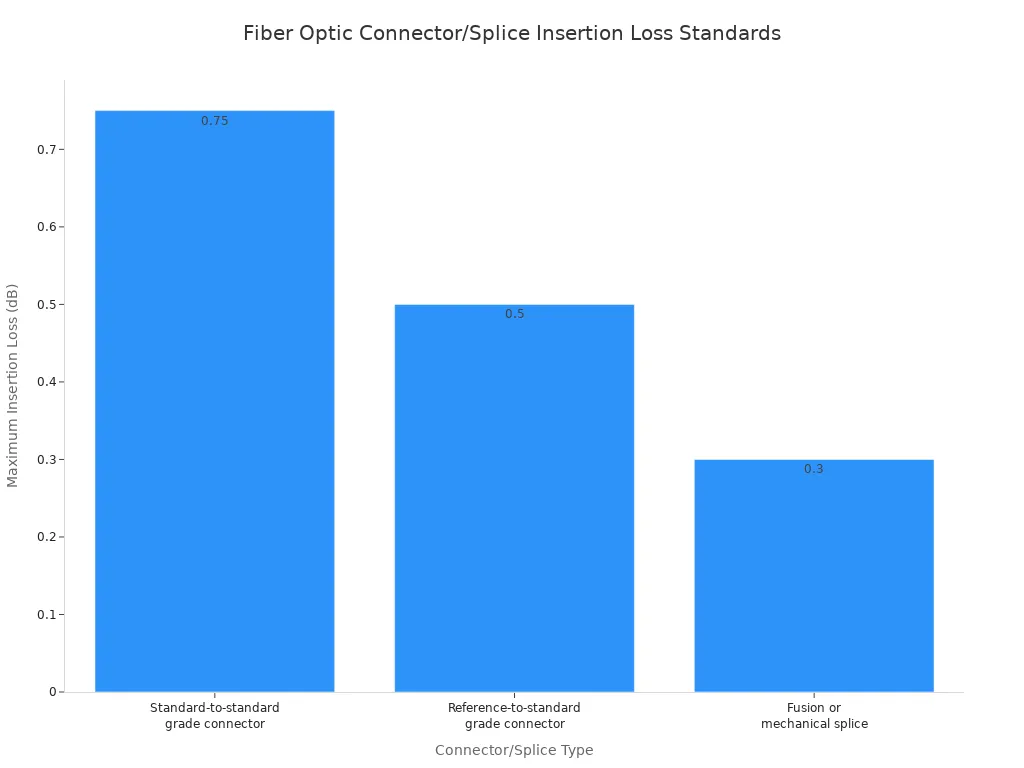
Acceptable loss limits vary by fiber type and standards. For multimode fiber, a reading under 3.0 dB/km at 850nm is good. For single-mode fiber, a reading under 0.5 dB/km at 1310nm or 1550nm is ideal.
Implementing Robust Quality Control for Fiber Optic Cable Imports

Implementing robust quality control measures is essential for successful Fiber Optic Cable imports. These measures ensure the product meets all performance and durability requirements. A comprehensive quality control strategy covers the entire production cycle, from raw materials to final shipment.
Ensuring Raw Material Inspection for Fiber Optic Cable Components
Quality begins with the raw materials. Manufacturers must implement strict inspection protocols for all incoming components. The integrity of each raw material directly impacts the final product’s performance and longevity.
Critical raw materials for optical fiber manufacturing include:
- Highly purified silicon dioxide (SiO₂), essentially refined sand, forms the core of the optical fiber itself. Its purity determines the fiber’s optical properties.
- Acrylate is used for the two protective coating layers applied immediately after fiber drawing. These coatings protect the delicate glass fiber from physical damage.
- Thermoplastic forms buffer tubes, which provide an additional layer of protection around the coated fibers.
- Fiber Reinforced Plastic (FRP) rods often serve as a central strength member. Buffer tubes are stranded around this member, providing structural integrity.
- Water-blocking yarns and gels are added to prevent moisture ingress, which can degrade fiber performance.
- Aramid yarn provides tensile strength, especially in aerial cables, allowing them to withstand pulling forces.
- Corrugated steel tape offers rodent protection in direct buried cables, preventing damage from pests.
- Polyethylene (PE) typically forms the outer jacket. Specific properties, such as UV resistance or low-smoke, zero-halogen (LSZH) characteristics, depend on the installation environment.
Manufacturers must verify the specifications and quality of these materials before they enter the production line. This proactive approach prevents defects from propagating into the finished product.
Demanding Pre-Shipment Testing and Reviewing Fiber Optic Cable Reports
Pre-shipment testing provides a final verification of product quality before dispatch. Buyers should demand comprehensive testing and review all associated reports. Testing fiber optic cables on the reel before installation is crucial. This process identifies potential damage from shipping or manufacturing defects.
An Optical Time Domain Reflectometer (OTDR) is a key tool for pre-shipment testing. It performs single-ended testing on the reel to determine cable length and detect significant loss events. This is possible even if only one end of the cable is accessible. Testing the fiber on a reel before pulling it is a recommended practice. It ensures the cable has not been damaged during shipment, saving time and money. Visual inspection for signs of damage, such as cracked or broken reels or kinks in the cable, should also be performed.
It is essential to test fiber optic cables after shipping and handling. Damage can occur during transit. Using an OTDR to create an optical profile of each fiber while the cable is still on the shipping reel provides a permanent record. This helps detect damage before installation.
A comprehensive pre-shipment test report should include:
- Continuity Test: This test ensures no damage occurred during shipment. It is generally sufficient for pre-installation verification.
- OTDR Testing: This is required if any visible damage is observed on the cable reels. It verifies the cable’s integrity and pinpoints any issues.
Understanding Relevant Standards and Certifications for Fiber Optic Cable
Adherence to relevant standards and certifications is non-negotiable for quality assurance. These benchmarks ensure products meet international performance and safety criteria. Several organizations establish these critical guidelines.
International standards organizations for fiber optic cables include:
- ISO/IEC: This body develops and facilitates standards for information technology equipment interconnection. JTC1/SC25/WG 3 oversees customer premises cabling.
- IEC Technical Committee (TC) 86: This committee prepares standards for fiber-optic systems, modules, devices, and components. It has three subcommittees:
- SC 86A focuses on Fibers and Cables.
- SC 86B deals with Interconnecting Devices and Passive Components.
- SC 86C handles Systems and Active Devices.
- Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): This global professional organization publishes standards for cabling and networking technologies, such as the IEEE 802.3 group for Ethernet standards.
- InterNational Committee for Information Technology Standards (INCITS): This international organization sets standards for storage, transfer, and security impacting structured cabling systems.
- European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC): This body publishes the EN 50173 series standards for network cabling systems, including design and installation. These standards align with ISO/IEC.
- ITU-T: The Telecommunication Standardization Sector of ITU publishes technical reports on optical fibers, cables, and systems.
- The Fiber Optic Association (FOA): This organization creates its own basic standards for widely used tests and topics. It responds to concerns about the cost and meaning of other standards.
Key certifications are also vital for market entry and compliance:
| Market | Certification | Primary Focus |
|---|---|---|
| North America | UL | Safety and fire protection standards |
| North America | ETL | North American safety standards compliance |
| Europe | CPR | Fire performance in buildings |
| Europe | TÜV | Mechanical endurance, electrical safety, environmental resistance |
| Global | RoHS | Restriction of hazardous materials |
| Global | REACH | Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals |
These certifications, such as UL-Listed (Underwriters Laboratories) and ETL-Listed (Intertek) for North America, ensure safety and performance. RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) are European directives restricting hazardous materials and overseeing recycling. REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) is another critical European regulation. Manufacturers must provide valid certification documents for all products.
Prioritizing quality assurance throughout the Fiber Optic Cable import process remains crucial. Strategic supplier selection and rigorous quality checks are essential for reliable Fiber Optic Cable imports. These proactive measures ensure high-quality products and long-term performance for your critical network infrastructure.
FAQ
How does one verify a Chinese fiber optic cable manufacturer’s legitimacy?
Buyers verify legitimacy through comprehensive certifications like ISO 9001 and IEC 60794. They also conduct factory audits and assess transparent communication.
Which fiber optic cable specifications are most critical for quality?
Critical specifications include cable type, fiber core brand, virgin jacket materials, and precise attenuation and loss limits. These ensure optimal performance.
Why is pre-shipment testing essential for imported fiber optic cables?
Pre-shipment testing, often with an OTDR, verifies cable integrity before installation. It detects shipping damage or manufacturing defects, saving time and cost.
Post time: Dec-27-2025
